React Hooks useState 源码
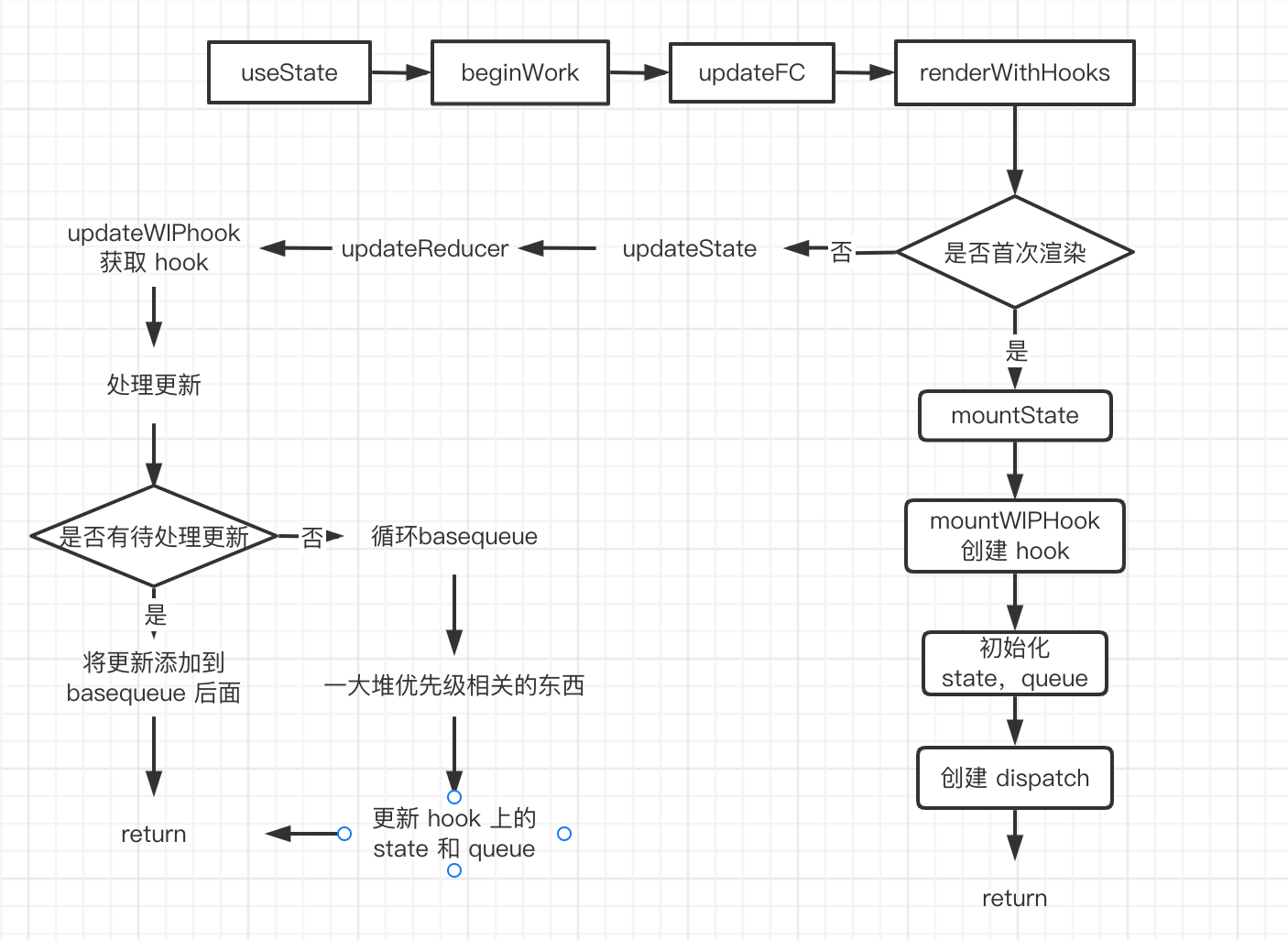
在 React Hooks 流程概览那篇文章中,介绍了 Hooks 的入口,以及 renderWithHooks 方法, 这个方法会在 updateComponent 的时候被调用,判断当前的状态,是 mount 还是 update 阶段会给 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 挂不同的 Hooks 对象合集
对于 useState 而言
在 mount 阶段,执行的 useState 方法,就相当于 HooksDispatcherOnMount 里的 mountState
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
useState: mountState,
};在 update 阶段,执行的 useState 方法,就相当于是 HooksDispatcherOnUpdate 里的 updateState
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
useState: updateState,
};在 mount 阶段的 mountState
hooks 的代码都比较短,都不需要删减了,真好 这是 FC 中调用
useState时,mount阶段调用的mountState方法
Hooks API 内部都会首先创建一个 hook 对象,一些状态、缓存函数、副作用都会绑定在这个 hook 对象上来实现组件状态的存储
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
// 创建新的 hook 对象,返回当前的 workInProgressHook
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
// 如果 useState 的传参是个 Function,那么就执行这个 Function
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
// $FlowFixMe: Flow doesn't like mixed types
initialState = initialState();
}
// 记录当前 useState 的返回结果
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
// 新建 queue 队列
const queue: UpdateQueue<S, BasicStateAction<S>> = {
pending: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
};
hook.queue = queue;
const dispatch: Dispatch<
BasicStateAction<S>,
> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchSetState.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber, // 这是一个全局变量,初始化为 workInProgress,用来绑定 fiber 和 queue
queue,
): any));
// 返回
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}React 有一个专门的函数来生成 hook ,名为 mountWorkInProgressHook,也就是上面看到的那个
在 mount 时
- 会执行
mountWorkInProgressHook方法创建一个新的 hook 对象 memoizedState和baseState赋值为初始化state- 创建一个队列
- 创建一个
dispatch也就是state的更新函数 - 将 Fiber 和 queue 绑定到
dispatch上 - 返回
state以及dispatch组成的数组
下面会重点讲解几个重要的方法
mountWorkInProgressHook 方法
在上面我们知道了 mountWorkInProgressHook 会创建一个新的 hook 对象,那么是如何创建的呢?
也很短,我真的爱了
// 创建新的 hook 对象,返回当前的 workInProgressHook
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
};
// workInProgressHook 是全局对象,因此只有第一次打开页面,它才为空
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list
// 链表上的第一个 hook
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list
// 已经存在 workInProgressHook 那就接在 next 指针下
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}- 首先会创建一个 Hook 对象
- 如果是首次的第一个 hook 的话,也就是
workInProgressHook还是空的情况下,就直接赋值给currentlyRenderingFiber上的memoizedState - 如果已经存在,那就接到 next 上面,形成链表
这里的 currentlyRenderingFiber 就标记着当前正在渲染的组件,而 Fiber.memoizedState 就保存了 hook 链表的头节点。
dispatchSetState 方法
在 mountState 中,通过 dispatchSetState 创建一个 dispatch 触发器,来更新 state,在创建 dispatch 触发器的时候,绑定了当前的 Fiber 节点,和新的 queue 队列
function dispatchSetState<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
) {
// 当前 Fiber 的更新优先级
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);
// 创建一个新的 Update
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
action,
hasEagerState: false,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
// 如果是 render 阶段的更新会执行 enqueueRenderPhaseUpdate
if (isRenderPhaseUpdate(fiber)) {
enqueueRenderPhaseUpdate(queue, update);
} else {
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
if (
fiber.lanes === NoLanes &&
(alternate === null || alternate.lanes === NoLanes)
) {
// 计算下一个 State,如果和当前的相同,那就退出渲染
const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
let prevDispatcher;
try {
const currentState: S = (queue.lastRenderedState: any);
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
update.hasEagerState = true;
update.eagerState = eagerState;
if (is(eagerState, currentState)) {
enqueueConcurrentHookUpdateAndEagerlyBailout(fiber, queue, update);
return;
}
}
}
}
// 获取当前的 Fiber,同步任务会立即执行,异步会走 scheduler
const root = enqueueConcurrentHookUpdate(fiber, queue, update, lane);
if (root !== null) {
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, fiber, lane, eventTime);
entangleTransitionUpdate(root, queue, lane);
}
}
markUpdateInDevTools(fiber, lane, action);
}原来当每一次改变 state ,底层会做这些事。
- 首先每一次调用
dispatchSetState都会先创建一个Update对象 ,然后把它放入待更新pending队列中。 - 然后判断如果当前的 fiber 正在更新,那么也就不需要再更新了。
- 反之,当前 fiber 没有更新任务,那么会计算新的
state和上一次state进行对比- 如果相同,那么直接退出更新。
- 如果不相同,那么发起更新调度任务。这就解释了,为什么函数组件 useState 改变相同的值,组件不更新了。
值得注意的是 isRenderPhaseUpdate(fiber) 方法,它是对 Fiber 调度的处理,如果 fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber 返回 true
也就是在 render 的时候触发的更新,可以理解为:当前更新周期中又产生了新的更新
function isRenderPhaseUpdate(fiber: Fiber) {
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
return (
fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber ||
(alternate !== null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber)
);
}如果是这种 re-render 的情况的话,那么会执行 enqueueRenderPhaseUpdate 方法,
function enqueueRenderPhaseUpdate<S, A>(
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
update: Update<S, A>,
) {
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass = didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = true;
const pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
}在这个方法里首先会对 didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass 进行赋值
如果 didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass 为 true,就会循环计数 numberOfReRenders 来记录 re-render 的次数。 如果你的循环次数过多的话,React 会终止并且提示循环了
然后会维护 queue 链表
queue 是一个环形链表
queue.pending指向最近一次更新pending.next指向第一次更新
如果不是 render 阶段的更新,就会计算下一阶段的 state -> eagerState 和 currentState 对比
- 如果相同,那么直接退出更新。
- 如果不相同,那么发起更新调度任务。这就解释了,为什么函数组件 useState 改变相同的值,组件不更新了。
eagerState 是根据 queue 上的各个参数(reducer、上次计算出的 state)计算出来的,然后挂载到 update 上
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
update.hasEagerState = true;
update.eagerState = eagerState;接着在 React 中是通过一个 is 方法,来判断 state 是否相同的,这是一个浅比较,因此在数组对象这种引用类型的 state 时,需要特别注意
function is(x: any, y: any) {
return (
(x === y && (x !== 0 || 1 / x === 1 / y)) || (x !== x && y !== y) // eslint-disable-line no-self-compare
);
}大体流程就是这样 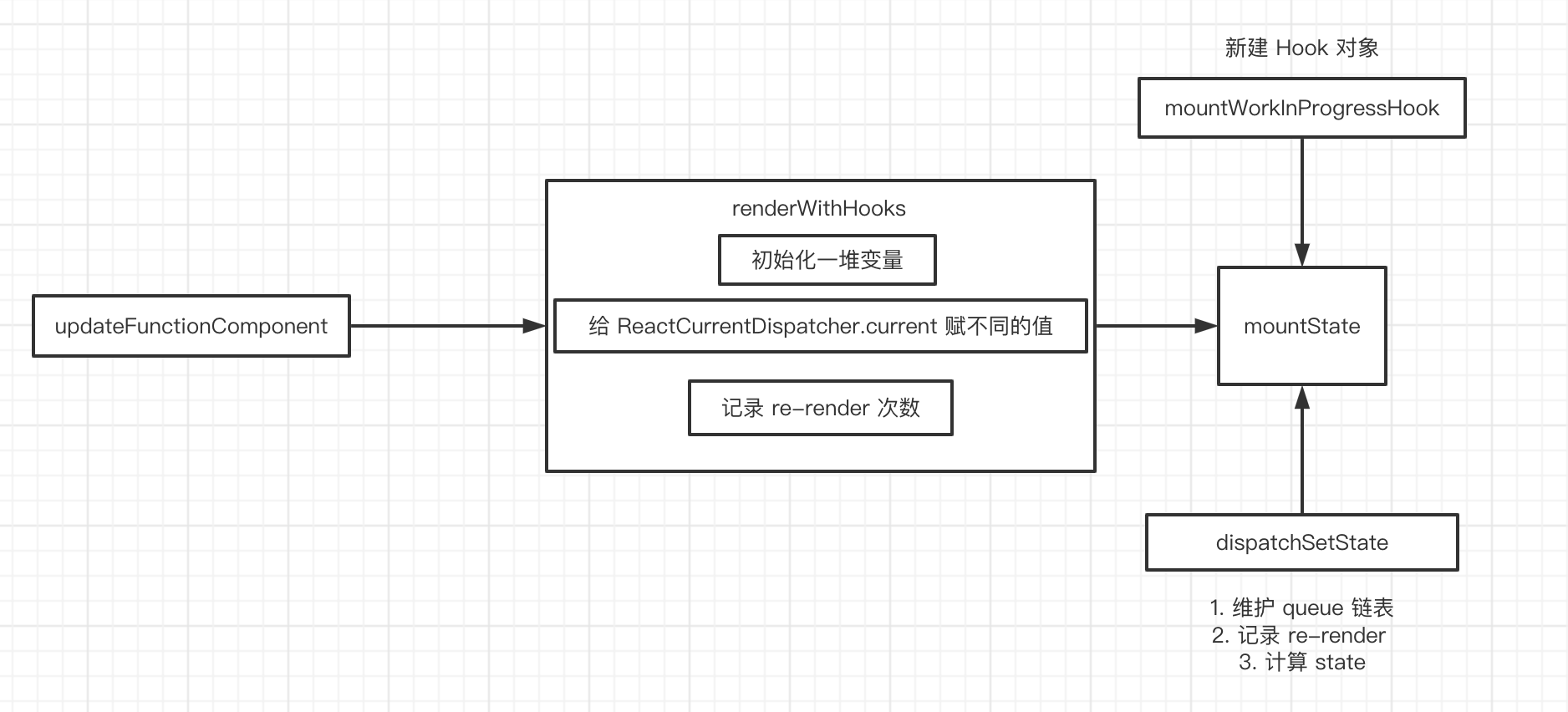
在 update 阶段,updateState
在讲完了 mount 的流程,接下来开始 update 时的流程
当我们使用 useState 返回的 dispatchSetState 来更新 state 时,就会触发 update 的流程
- 例如下面的例子中,我们通过
click事件调用setNumber相当于触发了一次dispatchSetState
export default function Index(){
const [ number , setNumber ] = useState(0)
const handleClick=()=>{
setNumber(num=> num + 1 ) // num = 1
}
return <div>
<button onClick={() => handleClick() } >点击 { number } </button>
</div>
}在前面我们知道,在 renderWithHooks 中会判断是 update 还是 mount 阶段,赋予不同的 Hooks 对象 这里我们是 update 阶段,会调用 HooksDispatcherOnUpdate 里的 useState,也就是 updateState
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
useState: updateState,
...
};updateState 其实调用的就是 updateReducer,所以我们说 useState 是一个特殊的 updateReducer。
也可以说是一个内置了 reducer 的 useReducer
function updateState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, (initialState: any));
}这里预支的 reducer 就是 basicStateReducer,
- 如果
action是一个Function那就返回Function的执行结果 - 否则就直接返回
action的值
function basicStateReducer<S>(state: S, action: BasicStateAction<S>): S {
// $FlowFixMe: Flow doesn't like mixed types
return typeof action === 'function' ? action(state) : action;
}下面来看看 updateReducer 这个方法,非常的长
有点长,保留了关键部分
function updateReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: I => S,
): [S, Dispatch<A>] {
// 获取当前的 hook 对象
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const queue = hook.queue;
queue.lastRenderedReducer = reducer;
// 获取当前 Fiber 上面的 hook 链表,以及 baseQueue
const current: Hook = (currentHook: any);
let baseQueue = current.baseQueue;
// 看看是不是还有没有处理的更新,有的话添加到 queue 里
const pendingQueue = queue.pending;
if (pendingQueue !== null) {
if (baseQueue !== null) {
// 把更新添加到队列后面,注意 queue 是一个环状链表
...
}
current.baseQueue = baseQueue = pendingQueue;
queue.pending = null;
}
// 没有产生新的 update,根据优先级来处理 update,这个在前面的状态更新也有具体讲解
if (baseQueue !== null) {
//初始化一堆变量
...
do {
// 遍历我们之前挂载到 fiber.memoizedState.queue.pending 上的环状链表,并得到最后的 newState
const updateLane = removeLanes(update.lane, OffscreenLane);
const isHiddenUpdate = updateLane !== update.lane;
// 判断是否能够跳过当前 update
const shouldSkipUpdate = isHiddenUpdate
? !isSubsetOfLanes(getWorkInProgressRootRenderLanes(), updateLane)
: !isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane);
if (shouldSkipUpdate) {
// 低优先级的更新,把 update 拷贝添加到队列尾部,跳过这个 update
const clone: Update<S, A> = {...};
// 维护 queue 双向链表
...
// 跳过
markSkippedUpdateLanes(updateLane);
} else {
// 高优先级的更新,赋值一份当前的 update
if (newBaseQueueLast !== null) {
const clone: Update<S, A> = {...};
newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone;
}
// 计算新的 state
...
}
// 下一个 update
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null && update !== first);
...
// 更新 hook、queue 上的相关属性,也就是将最新的这个 state 记录下来,这样下次更新的时候可以这次为基础再去更新
hook.memoizedState = newState;
...
}
...
const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch: any);
// 返回 state 和 dispatch
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}可以看到这里面处理了很多种情况,
- 在更新时有新的更新,会添加到 baseQueue 队列中,也就是 rerender
- 在处理更新中没有产生新的 update,根据优先级处理 update
对于低优先级的 update,会添加到更新队列尾部,不会计算新的 state
对于高优先级的更新,也会加到更新队列尾部,但会计算新的更新
具体的状态更新的源码解析在前面有讲过了,这里跳过
主要来说一个 updateWorkInProgressHook 方法
updateWorkInProgressHook 方法
在 mount 时,也有一个类似的方法,用来获取 `hook,但是这里有一点点不一样,我们来看看具体的实现
function updateWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
// 获取当前 hook 的下一个 hook
let nextCurrentHook: null | Hook;
// currentHooks 是全局变量,在 update 时,会被置为 null,
if (currentHook === null) {
const current = currentlyRenderingFiber.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
nextCurrentHook = current.memoizedState;
} else {
nextCurrentHook = null;
}
} else {
nextCurrentHook = currentHook.next;
}
// workInProgressHook 也是全局变量,也是 null
let nextWorkInProgressHook: null | Hook;
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
nextWorkInProgressHook = currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState;
} else {
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
}
if (nextWorkInProgressHook !== null) {
// 如果 wip 已经初始化过了,那就
workInProgressHook = nextWorkInProgressHook;
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
} else {
// 如果hook 变多了,会终止,大概率是 if 中使用 hook
if (nextCurrentHook === null) {
throw new Error('Rendered more hooks than during the previous render.');
}
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
// 生成新的 hook
const newHook: Hook = {...};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// update 时的 wiphook 的第一个 hook
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = newHook;
} else {
// 非第一个 hook 加到链表里
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook;
}
}
return workInProgressHook;
}renderWithHooks 函数调用 FC 执行之前,workInProgressHook、currentHook 都为 null。 同时新的 fiber 的 memoizedState、updateQueue 都被重置为 null
workInProgressHook用于构建新的 hook 链表currentHook用于遍历上一次渲染构建的 hook 链表,即旧的链表,或者当前的链表(即和当前显示的页面对应的 hook 链表)
可以类比 WIP Fiber Tree 的构建过程
例如一个 FC 里调用了 useState 的 dispatch 在更新的时候获取 wip hook 的时候,此时 currentHook 为 null,因此我们需要初始化它指向旧的 hook 链表的第一个 hook 对象。
if (currentHook === null) {
var current = currentlyRenderingFiber.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
nextCurrentHook = current.memoizedState;
} else {
nextCurrentHook = null;
}
}
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;创建一个新的 hook 对象,复用上一次的 hook 对象的状态信息,并初始化 hook 链表
const newHook: Hook = {
memoizedState: currentHook.memoizedState,
baseState: currentHook.baseState,
baseQueue: currentHook.baseQueue,
queue: currentHook.queue,
next: null,
};
// 第一个 hook wiphook 为null
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = newHook;
} else {
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook;
}同时还有一点会让人不懂的地方,就是 nextWorkInProgressHook !== null 的判断,这个判断主要是用来区分 rerender 的情况
- 如果是在
render阶段,则会取下一个 hook 作为当前的hook,并返回 workInProgressHook,也就是 if 成立里的逻辑 - 如果是在
re-render阶段,则在当前处理周期中,继续取当前的workInProgressHook做更新处理,最后再返回workInProgressHook。
从更新渲染的过程也可以看出,hook 函数的执行是会遍历旧的 hook 链表并复用旧的 hook 对象的状态信息。 这也是为什么我们不能将 hook 函数写在条件语句或者循环中的根本原因,我们必须保证 hook 函数的顺序在任何时候都要一致
总结流程
FC 通过
renderWithHooks方法确定当前的 WIP Fiber 节点,通过current是否存在来判断是mount阶段还是update阶段,并设置相应的ReactCurrentDispatcher.current,来调用不同的 hook 函数在 FC 执行时,会执行对应的 hook 函数,FC 的 hooks 存放在 Fiber 节点的
memoizedState属性上,通过 next 属性连接形成单向链表在 hook 对象上的 queue 属性上,存放着 hook 的更新队列,他是一个环转链表,
padding指向最新的 Update
在 mount 时,通过 mountWorkInProgressHook 来创建一个新的 hook 对象,然后返回初始化的 state 和 dispatch
在 update 时,通过 updateWorkInProgressHook 来获取新的 hook 对象,这里会复用旧的 hook 状态
调用 dispatch 触发 action,发起更新任务调度,同时在 dispatchAction 里计算最新的 state,并更新 queue 环形链表,然后执行 scheduleUpdateOnFiber,进入调度,再次进入到 renderWithHooks,执行 updateState (实际上执行的是 updateReducer) ,得到新的 state 值返回,并重新计算渲染。
大体流程图