completeWork 工作流程
在上一节,我们已经讲过了 beginwork 阶段的工作流程,这一节来讲与 beginwork 相对的 completeWork 的工作流程
作为 render 的“归”阶段,需在 render 的“递”阶段结束后才会执行;换句话说,当 beginWork 返回 null 值,即当前节点无(或无需关注)当前节点的子Fiber节点时,才会进入到 render 的 completeWork 阶段
概述
render 阶段就是通过深度优先遍历的方式,来执行 Fiber 节点的 beginWork 和 completeWork。在 beginWork完成后会创建子 Fiber 节点,节点上可能会存在 effectTag(即 flags),同时在 Diff 阶段之后,workInProgress 节点就会进入 completework 阶段。这个时候拿到的 workInProgress 节点都是已经被调和过的,也就意味着对于某个节点来说它的 Fiber 的形态已经基本确定了
只有当 beginWork 返回 null ,即当前节点无子 Fiber 节点时,才会进入 render 的 completeWork 阶段
在开始 completeWork 之前,需要先明确几点
- 在
beginWork阶段的reconcileChildren阶段中,会为workInProgress节点标记effectTag - 对于
HostComponent和HostText来说,Fiber 形态的改变,并不会影响 DOM 节点的变化
因此,completeWork 的工作可以划分为以下几点
- 构建或更新 DOM 节点
- 自下而上收集
effectTag,形成effectList链表,最终收集到rootFiber上
对于 workInProgress 节点更新出错的时候,会对出错的节点采取措施,会有额外的错误处理过程
流程概览
和 beginWork类似,归阶段的入口在 completeUnitOfWork,在这个函数内部有一个循环,会从下到上的遍历 workInProgress 节点,依次处理
对于正常的 workInProgress 节点,会执行 completeWork,这其中会对 Host Component 类型的节点完成更新 props、事件绑定等 DOM 操作
异常节点会进入 unwindWork进行处理
Host Component 就是 DOM 组件对应的 Fiber 节点
function completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
let completedWork = unitOfWork;
do {
const current = completedWork.alternate;
const returnFiber = completedWork.return;
if ((completedWork.flags & Incomplete) === NoFlags) {
// 如果 workInProgress 节点没有出错的逻辑
setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(completedWork);
let next;
// 对节点进行completeWork,生成DOM,更新props,绑定事件
// 省略判断的逻辑,最终都是执行 completeWork
next = completeWork(current, completedWork, subtreeRenderLanes);
if (next !== null) {
// 任务被挂起
workInProgress = next;
return;
}
} else {
// unwindWork 处理更新错误的逻辑
const next = unwindWork(completedWork, subtreeRenderLanes);
...
}
// 查找有没有兄弟节点,如果有则进行 beginWork -- completeWork
const siblingFiber = completedWork.sibling;
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
workInProgress = siblingFiber;
return;
}
// 若没有兄弟节点,那么向上回到父级节点进行 completeWork
completedWork = returnFiber;
workInProgress = completedWork;
} while (completedWork !== null);
// 到了 rootFiber 节点,标记整棵树完成
if (workInProgressRootExitStatus === RootIncomplete) {
workInProgressRootExitStatus = RootCompleted;
}
}completeUnitOfWork的主要逻辑在于对整个 “归”阶段进行控制
- 调用
completeWork方法来完成对当前Fiber节点对应的 DOM 节点的创建等操作 - 设置 subtreeFlags 标识子树是否有更新(替代了原先的 effect List 副作用链表)
- 若当前 Fiber 节点有 sibling 节点,则进入该节点的 performUnitOfWork 开始一轮子树的 beginWork
- 如果没有 sibling 节点,则会开始父节点的 completeWork
- 直到 rootFiber 节点,completeWork 工作完成
completeWork 主要工作
对于 React 来说,大部分的节点最终都是 DOM 节点,因此对于 HostComponent 的处理至关重要,在 completeWork 中会对不同的 tag 做不同的处理,对于 Host Component 和 HostText 的处理都是为其创建对应的 DOM 节点,处理方法都会分为更新和创建,如果 current 存在并且 workInProgress.stateNode 存在,说明对应的 DOM 节点已经存在,会进入更新的逻辑,
function completeWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
...
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
case LazyComponent:
case SimpleMemoComponent:
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case Fragment:
case Mode:
case Profiler:
case ContextConsumer:
case MemoComponent:
return null;
case ClassComponent: {
// ...省略
return null;
}
case HostComponent: {
...
if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
// 更新
} else {
// 创建
}
return null;
}
case HostText: {
const newText = newProps;
if (current && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
// 更新
} else {
// 创建
}
return null;
}
case SuspenseComponent:
...
}
}完整流程图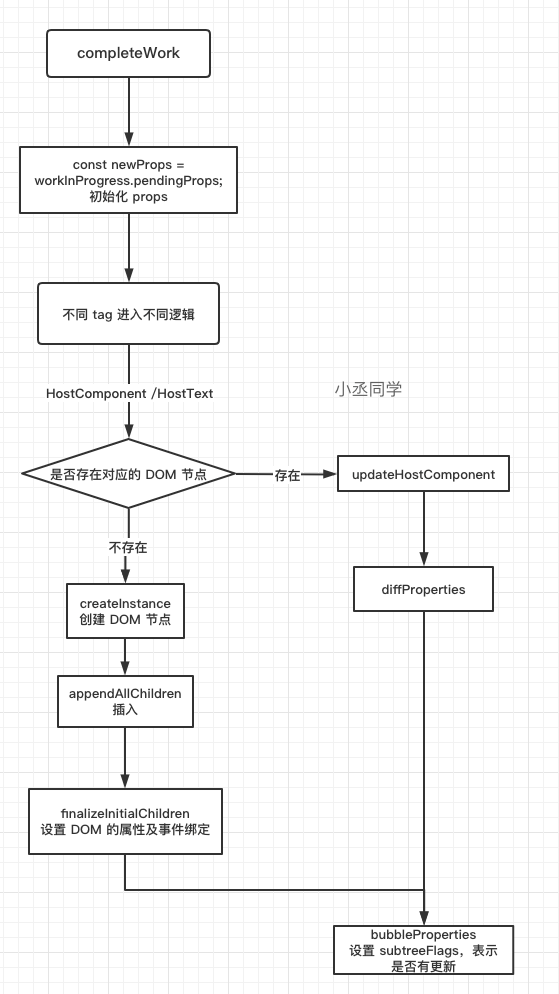
处理 Host Component
completeWork 处理的是 Diff 算法之后产生的新 Fiber,因此对于 completeWork 来说,接受到的 workInProgress 可能是需要创建,也有可能是更新。因此需要判断出是执行更新 DOM 的过程,还是创建 DOM 的过程。
对于需要执行创建操作的节点来说,还需要进行额外的插入操作,与整棵 DOM 树进行连接
case HostComponent: {
popHostContext(workInProgress);
const rootContainerInstance = getRootHostContainer();
const type = workInProgress.type;
if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
// 已有节点,进入更新 DOM 的逻辑
updateHostComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
);
if (current.ref !== workInProgress.ref) {
markRef(workInProgress);
}
} else {
// 如果没有新的props并且stateNode为null, 可能是React发生了内部错误
...
const currentHostContext = getHostContext();
const wasHydrated = popHydrationState(workInProgress);
if (wasHydrated) {
// SSR 相关
} else {
// fiber 不存在对应的 DOM 节点,进行创建
const instance = createInstance(
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
currentHostContext,
workInProgress,
);
// 插入
appendAllChildren(instance, workInProgress, false, false);
// 挂载到 Fiber 上
workInProgress.stateNode = instance;
if (
// 设置 DOM 对象的属性和事件绑定
finalizeInitialChildren(
instance,
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
currentHostContext,
)
) {
// 设置fiber.flags标记(Update)
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
}
if (workInProgress.ref !== null) {
// 设置fiber.flags标记 (Ref)
markRef(workInProgress);
}
}
// 副作用相关
bubbleProperties(workInProgress);
return null;
}mount 时
mount 时的主要逻辑包括三个
- 为 Fiber 节点生成对应的 DOM 节点
- 将子孙节点插入当前生成的 DOM 节点中(因为自下而上)
- 处理 props 以及事件绑定
createInstance
通过调用 createInstance 创建新的 DOM 节点
export function createInstance(
type: string,
props: Props,
rootContainerInstance: Container,
hostContext: HostContext,
internalInstanceHandle: Object,
): Instance {
let parentNamespace: string;
...
// 确定该DOM节点的命名空间
parentNamespace = ((hostContext: any): HostContextProd);
// 创建 DOM 元素
const domElement: Instance = createElement(
type,
props,
rootContainerInstance,
parentNamespace,
);
// 缓存 Fiber 节点
precacheFiberNode(internalInstanceHandle, domElement);
//更新 fiber 节点的 props, 在 DOM 实例上
updateFiberProps(domElement, props);
return domElement;
}appendAllChildren
在创建好了新的 DOM 节点后,会执行 appendAllChildren 将所有子节点插入到刚刚创建好的 DOM 节点上,在全部插入完毕后会执行 workInProgress.stateNode = instance; 将 DOM 节点挂载到 Fiber 节点的 stateNode 属性上
需要注意的是 completeWork 是自下而上执行的,这里的 DOM 节点插入,是将已经创建好的 子 DOM 节点,插入到当前刚创建的 DOM 节点上,建立起连接
同时对于整体而言,DOM 节点的插入是深度优先遍历进行的,整个的 DOM 节点插入的过程并没有将真实的 DOM 节点插入到真实的页面上,只是在内存中操作,最后挂载到了 stateNode 上。真实的 DOM 操作发生在 commit 阶段进行
appendAllChildren = function (parent, workInProgress, needsVisibilityToggle, isHidden) {
// 拿到当前工作单元的child Fiber节点
var node = workInProgress.child;
while (node !== null) {
if (node.tag === HostComponent || node.tag === HostText) {
// 调用 parent.appendChild(node.stateNode);
appendInitialChild(parent, node.stateNode);
}
...
if (node === workInProgress) { // 如果是当前工作单元, 插入完毕
return;
}
while (node.sibling === null) { // 没有兄弟节点则Fiber向上冒泡
if (node.return === null || node.return === workInProgress) {
return;
}
node = node.return;
}
node.sibling.return = node.return; // 把兄弟节点的return节点赋值给父节点
node = node.sibling; // 把node赋值为兄弟节点
}
};在首屏渲染时,会将所有的子孙 DOM 节点插入到新生成的 DOM 节点下,当 completeWork 执行到 rootFiber 时,我没以及在内存中构建好了一颗 DOM 树,这样只需要一个 Placement 的 effectTag,就可以完成首屏渲染
finalizeInitialChildren
然后执行的是 finalizeInitialChildren 方法
从下面的代码段,我们可以很清晰地看到 finalizeInitialChildren 主要分为两个步骤:
- 执行
setInitialProperties方法
注意:该方法是会真正将 DOM 属性挂载到 DOM 节点上的,也会真正地调用 addEventListener 把事件处理回调绑定在当前 DOM 节点上的。
- 执行
shouldAutoFocusHostComponent方法:返回props.autoFocus的值(仅 button / input / select / textarea 支持)。
export function finalizeInitialChildren(
domElement: Instance,
type: string,
props: Props,
rootContainerInstance: Container,
hostContext: HostContext,
): boolean {
setInitialProperties(domElement, type, props, rootContainerInstance);
return shouldAutoFocusHostComponent(type, props);
}setInitialProperties方法,来判断 props 是否合法,并对 DOM 节点进行一些操作,并把初始化的属性赋值到当前的 DOM 上,同时也会把事件处理回调绑定在当前的 DOM 节点上
function setInitialProperties(domElement, tag, rawProps, rootContainerElement) {
var isCustomComponentTag = isCustomComponent(tag, rawProps);
{
validatePropertiesInDevelopment(tag, rawProps);
}
var props;
switch (tag) {
...
// 跳过一些dom节点的判断逻辑
default:
props = rawProps;
}
// 判断 props 是否合法
assertValidProps(tag, props);
// 设置初始化的dom属性
setInitialDOMProperties(tag, domElement, rootContainerElement, props, isCustomComponentTag);
switch (tag) {
case 'input':
track(domElement);
postMountWrapper(domElement, rawProps, false);
break;
...
break;
}
}在 setInitialDOMProperties 函数中会调用新的 props ,并对每个 propKey 做特定的赋值操作,并会调用 setValueForProperty 来为创建好的 DOM 元素设置属性(node.setAttribute)
处理 ref
判断 ref 是否存在,如果存在 ref 调用 markRef,会为当前的 fiber 上的 flags 设置对应的标识
function markRef(workInProgress: Fiber) {
workInProgress.flags |= Ref;
if (enableSuspenseLayoutEffectSemantics) {
workInProgress.flags |= RefStatic;
}
}bubbleProperties
最后执行 bubbleProperties,根据 fiber.child 和 fiber.child.sibling 更新subtreeFlags 和childLanes,主要是为了标记子树有没有更新,这样就可以通过 fiber.subtreeFlags 来快速判断子树中是否有副作用,不需要深度优先遍历去搜索
let child = completedWork.child;
while (child !== null) {
newChildLanes = mergeLanes(
newChildLanes,
mergeLanes(child.lanes, child.childLanes),
);
subtreeFlags |= child.subtreeFlags & StaticMask;
subtreeFlags |= child.flags & StaticMask;
child.return = completedWork;
child = child.sibling;
}
}
completedWork.subtreeFlags |= subtreeFlags;subtreeFlags 是 fiber 结构中的一个属性,代表子树中包含的副作用,避免深度遍历
在 React 17 版本中,用 subTreeFlags 来替代了原先 finishWork.firstEffect 的副作用链表
update 时
在 update 时,Fiber 节点已经存在了对应的 DOM 节点,因此不需要创建 DOM 节点,只需要对属性进行更新即可,因为节点已经存在,不存在删除和新增的情况
主要会处理 props,包括 style、children、onClick 等,并会将处理好的 props 赋值给 updatePayload,最后保存到 updateQueue 上
在 completeWork 中,更新会进入 if 的逻辑,执行 updateHostComponent对 DOM 节点的属性进行更新
if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
// 已有节点,进入更新 DOM 的逻辑
updateHostComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
);
if (current.ref !== workInProgress.ref) {
markRef(workInProgress);
}
}
...
}updateHostComponent
在 updateHostComponent 函数中会将最终需要 update 的 props 挂载到 update Queue 中,在 commit 阶段进行更新,在这里最重要的就是通过执行 prepareUpdate 去计算需要更新的新属性
updateHostComponent = function (
current: Fiber,
workInProgress: Fiber,
type: Type,
newProps: Props,
rootContainerInstance: Container,
) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps; // 获取 props
// props 相同,进入了 bailout 阶段,跳过
if (oldProps === newProps) {
return;
}
const instance: Instance = workInProgress.stateNode; // 获取 DOM 实例
const currentHostContext = getHostContext();
const updatePayload = prepareUpdate(
instance,
type,
oldProps,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
currentHostContext,
);
// 最终新属性被挂载到 updateQueue 上, commit 阶段使用
workInProgress.updateQueue = (updatePayload: any);
if (updatePayload) {
//标记更新 flags |= Update
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
};prepareUpdate
prepareUpdate函数会直接调用 diffProperties来 diff 出 props 的不同
export function prepareUpdate(
domElement: Instance,
type: string,
oldProps: Props,
newProps: Props,
rootContainerInstance: Container,
hostContext: HostContext,
): null | Array<mixed> {
...
return diffProperties(
domElement,
type,
oldProps,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
);
}diffProperties
diffProperties会返回一个 updatePayload 数组,第 i 项是对应的 propKey,第 i + 1 项是对应的 value
updatePayload = ["props", null, "style", {"color":"pink"} ]当存在 updatePayload 时,意味着这个 HostComponent 存在着更新,会调用 markUpdate 设置 flags(effectTag)进行标识,在 commit 阶段进行更新
执行完这个diffProperties, 再执行bubbleProperties, 然后就结束了当前节点的 completeWork 阶段
流程结束
至此,render 阶段的工作全部完成了,在 performSyncWorkOnRoot 函数中 fiberRoot 被传递给 commitRoot,开启了 commit 阶段的工作
commitRoot(root);总结
completeUnitOfWork方法主要工作是循环执行completeWork,父元素为空或存在 sibling 节点,会先生成 sibling 对应的 Fiber 节点completeWork的主要工作是根据 Fiber 节点生成对应的 DOM 节点,并连接起子节点- 在更新时会对 DOM 节点对应的新旧 props 进行 diff,并打上
updatePayload - 最终结束
completeUnitOfWork执行,进入commit阶段
