Scheduler 源码解析
INFO
终于开始写这篇了,只想快快的把这个系列收尾了,这篇文章可能会引用比较多的内容,天色已晚,不宜久留
上篇讲了 Scheduler 的实现原理,下面来看看它是如何实现的
详细流程
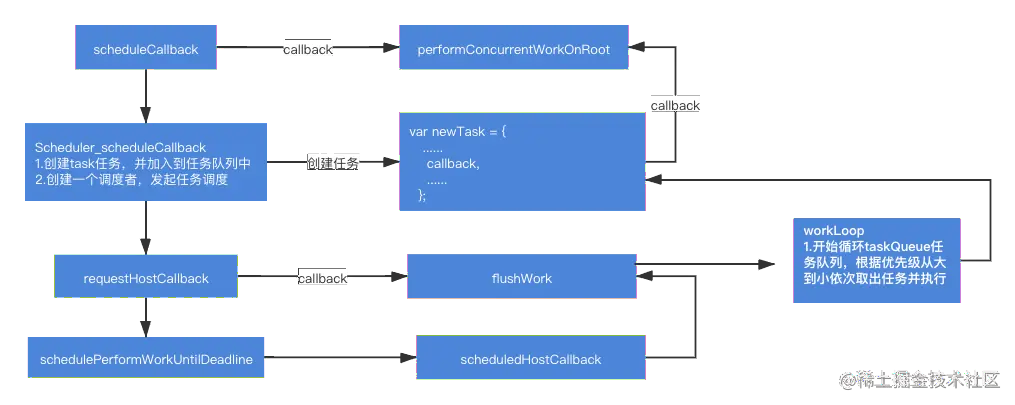
React 通过下面的代码让 Fiber 树的构建进入调度流程:
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number){
...
let schedulerPriorityLevel;
// 通过lanesToEventPriority函数将lane优先级转化为Scheduler优先级
switch (lanesToEventPriority(nextLanes)) {
case DiscreteEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = ImmediateSchedulerPriority;
break;
case ContinuousEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = UserBlockingSchedulerPriority;
break;
case DefaultEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority;
break;
case IdleEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = IdleSchedulerPriority;
break;
default:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority;
break;
}
//将react与scheduler连接,将react产生的事件作为任务使用scheduler调度
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
}在这里会做一次优先级的转化,将 React 的优先级,转成 Scheduler 的优先级
因为 React 和 Scheduler 都是相对独立的,它们自己内部都有自己的一套优先级机制,所以当 React 产生的事件需要被 Scheduler 调度时,需要将 React 的事件优先级转换为 Scheduler 的调度优先级。
Scheduler中的优先级
说到优先级,我们来看一下 Scheduler 自己的优先级级别,它为任务定义了以下几种级别的优先级:
export const NoPriority = 0; //没有优先级
export const ImmediatePriority = 1; // 立即执行任务的优先级,级别最高
export const UserBlockingPriority = 2; // 用户阻塞的优先级
export const NormalPriority = 3; // 正常优先级
export const LowPriority = 4; // 较低的优先级
export const IdlePriority = 5; // 优先级最低,表示任务可以闲置(在没有任务执行的时候,才会执行闲置的任务)任务优先级是计算任务过期时间的重要依据,事关过期任务在 taskQueue 中的排序。
过期时间是任务开始时间加上
timeout,而这个timeout则是通过任务优先级计算得出。
调度入口-scheduleCallback
接下来我们看看 scheduleCallback 内部代码:
function scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback) {
...
return Scheduler_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback);
}
function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) {
......
}这个方法就是 react 与 Scheduler 连接的函数。
Scheduler 中的任务管理队列
Scheduler 中有两个任务队列:timerQueue 和 taskQueue。 timerQueue 和 taskQueue 都是最小堆的数据结构。
- timerQueue:所有没有过期的任务会放在这个队列中。
- taskQueue:所有过期的任务会放在该队列中,并且按过期时间排序,过期时间越小则排在越前面,并且越先执行。
当 Scheduler 开始调度任务执行时,首先会从 taskQueue 过期任务队列中获取任务执行,一个任务执行完成则会从 taskQueue 中弹出,
当 taskQueue 中所有的任务都执行完成了,那么则会去 timerQueue 中检查是否有过期的任务,有的话则会拿出放到 taskQueue 中去执行。
下面来看一下具体的源码:
function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) {
var currentTime = getCurrentTime(); //当前时间
var startTime; //任务开始执行的时间
if (typeof options === 'object' && options !== null) {
var delay = options.delay;
if (typeof delay === 'number' && delay > 0) {
startTime = currentTime + delay;
} else {
startTime = currentTime;
}
} else {
startTime = currentTime;
}
var timeout; //任务延时的时间
...
var expirationTime = startTime + timeout; //任务过期时间
//以react产生的事件来创建一个新的任务
var newTask = {
id: taskIdCounter++,
callback, // callback = performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
priorityLevel,
startTime,
expirationTime,
sortIndex: -1,
};
if (startTime > currentTime) {
// This is a delayed task.
//将开始时间作为排序id,越小排在越靠前
newTask.sortIndex = startTime;
//将新建的任务添加进延时任务队列中
push(timerQueue, newTask);
if (peek(taskQueue) === null && newTask === peek(timerQueue)) {
if (isHostTimeoutScheduled) {
cancelHostTimeout();
} else {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = true;
}
// 创建一个timeout作为调度者
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime);
}
} else {
//将过期时间作为排序id,越小排在越靠前
newTask.sortIndex = expirationTime;
//将新建的任务添加进过期任务队列中
push(taskQueue, newTask);
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskStart(newTask, currentTime);
newTask.isQueued = true;
}
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled && !isPerformingWork) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
}
}
return newTask;
}scheduleCallback 中主要是创建一个新的任务,并且根据任务的开始时间来判断任务是否过期,针对未过期的任务则会添加到 timerQueue 中, 使用 startTimer 做为排序的依据。如果 taskQueue 中任务全部执行完成,则会调用 requestHostTimeout ,实际上这个函数是创建了一个 setTimeout, 把第一个任务的超时时间作为 setTimeout 的时间间隔调用 handleTimeout。
那么 handleTimeout 中又做了哪些事情,我们来看下源码:
function handleTimeout(currentTime) {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = false;
//检查延时任务队列中是否有已过期的任务,有的话则将过期任务拿出添加到过期任务队列中进行执行
advanceTimers(currentTime);
//isHostCallbackScheduled判断是否已经发起过调度,如果当前没有正在执行的调度,则会创建一个调度去执行任务
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled) {
if (peek(taskQueue) !== null) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
} else {
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
}
}
}handleTimeout 中主要是检查 timerQueue 中是否有已过期的任务,有的话则会将已过期的任务添加到 taskQueue 中去执行。这项工作主要是 advanceTimers 这个函数去来实现的:
function advanceTimers(currentTime) {
//检查延时任务队列中是否有已过期的任务,有的话则将过期任务拿出添加到过期任务队列中进行执行
let timer = peek(timerQueue);
while (timer !== null) {
if (timer.callback === null) {
// Timer was cancelled.
pop(timerQueue);
} else if (timer.startTime <= currentTime) {
// Timer fired. Transfer to the task queue.
pop(timerQueue);
timer.sortIndex = timer.expirationTime;
push(taskQueue, timer);
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskStart(timer, currentTime);
timer.isQueued = true;
}
} else {
// Remaining timers are pending.
return;
}
timer = peek(timerQueue);
}
}针对过期的任务,则会将过期时间作为排序依据,然后调用 requestHostCallback 函数创建调度者开始调度流程。
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled && !isPerformingWork) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
}创建调度者-requestHostCallback
function requestHostCallback(callback) {
scheduledHostCallback = callback;
if (!isMessageLoopRunning) {
isMessageLoopRunning = true;
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline();
}
}这里我们先记住 callback 是调用 requestHostCallback 传入的 flushWork 函数,会在后面调用。
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline 是创建调度者真正的函数,我们来看下它的实现:
let schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline;
if (typeof localSetImmediate === 'function') {
// 使用setImmediate的主要原因是因为在服务端渲染,MessageChannel会阻止nodejs的进程退出
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
localSetImmediate(performWorkUntilDeadline);
};
} else if (typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined') {
// 使用MessageChannel的原因是因为
// setTimeout如果嵌套的层级超过了 5 层,并且 timeout 小于 4ms,则设置 timeout 为 4ms。
const channel = new MessageChannel();
const port = channel.port2;
channel.port- onmessage = performWorkUntilDeadline;
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
port.postMessage(null);
};
} else {
//在以上方案都不能实现的时候,则降级使用setTimeout来实现创建调度者
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
localSetTimeout(performWorkUntilDeadline, 0);
};
}关于 setImmediate 和 MessageChannel 这里就不做详细介绍
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline 函数主要是创建一个调度者,并调用 performWorkUntilDeadline 函数发起任务的调度。 performWorkUntilDeadline 函数中则会调用任务的执行函数开始执行任务, 那么接下来我们则会重点讲解一下 任务的执行,中断和恢复 。
任务执行-performWorkUntilDeadline
它的作用是按照时间片的限制去中断任务,并通知调度者再次调度一个新的执行者去继续任务。
const performWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
if (scheduledHostCallback !== null) {
const currentTime = getCurrentTime();
startTime = currentTime;
const hasTimeRemaining = true;
let hasMoreWork = true;
try {
//调用scheduledHostCallback函数,开始任务的执行 scheduledHostCallback = flushWork
hasMoreWork = scheduledHostCallback(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime);
} finally {
if (hasMoreWork) {
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline();
} else {
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
scheduledHostCallback = null;
}
}
} else {
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
}
needsPaint = false;
};performWorkUntilDeadline 内部调用的 scheduledHostCallback 函数,是在调用 requestHostCallback 时赋值为了 flushWork 函数。
flushWork 作为真正去执行任务的函数,它会循环 taskQueue,逐一调用里面的任务函数。
接下来我们看一下 flushWork 函数中干了什么:
function flushWork(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) {
...
return workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime);
...
}其函数内部最终调用了 workLoop 函数,然后将 workLoop 的返回值返回了出去,也就是 performWorkUntilDeadline 中的 hasMoreWork 的值。从这里可以看出真正执行任务的地方就在 workLoop 函数中。
workLoop 调度循环
function workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) {
let currentTime = initialTime;
advanceTimers(currentTime);
// 获取taskQueue中最紧急的任务
currentTask = peek(taskQueue);
while (
currentTask !== null &&
!(enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused)
) {
if (
currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime &&
(!hasTimeRemaining || shouldYieldToHost())
) {
// This currentTask hasn't expired, and we've reached the deadline.
// 当前任务没有过期,但是已经到了时间片的末尾,需要中断循环
break;
}
const callback = currentTask.callback;
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
currentTask.callback = null;
currentPriorityLevel = currentTask.priorityLevel;
const didUserCallbackTimeout = currentTask.expirationTime <= currentTime;
markTaskRun(currentTask, currentTime);
const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout);
currentTime = getCurrentTime();
if (typeof continuationCallback === 'function') {
// 检查callback的执行结果返回的是不是函数,如果返回的是函数,则将这个函数作为当前任务新的回调。
// concurrent模式下,callback是performConcurrentWorkOnRoot,其内部根据当前调度的任务
// 是否相同,来决定是否返回自身,如果相同,则说明还有任务没做完,返回自身,其作为新的callback
// 被放到当前的task上。while循环完成一次之后,检查shouldYieldToHost,如果需要让出执行权,
// 则中断循环,走到下方,判断currentTask不为null,返回true,说明还有任务,回到performWorkUntilDeadline
// 中,判断还有任务,继续port.postMessage(null),调用监听函数performWorkUntilDeadline,
// 继续执行任务
currentTask.callback = continuationCallback;
markTaskYield(currentTask, currentTime);
} else {
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskCompleted(currentTask, currentTime);
currentTask.isQueued = false;
}
if (currentTask === peek(taskQueue)) {
pop(taskQueue);
}
}
advanceTimers(currentTime);
} else {
pop(taskQueue);
}
currentTask = peek(taskQueue);
}
// return 的结果会作为 performWorkUntilDeadline 中hasMoreWork的依据
// 高优先级任务完成后,currentTask.callback为null,任务从taskQueue中删除,此时队列中还有低优先级任务,
// currentTask = peek(taskQueue) currentTask不为空,说明还有任务,继续postMessage执行workLoop,但它被取消过,导致currentTask.callback为null
// 所以会被删除,此时的taskQueue为空,低优先级的任务重新调度,加入taskQueue
if (currentTask !== null) {
return true;
} else {
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
return false;
}
}workLoop 本身是一个大循环,这个循环非常重要。此时实现了时间切片和 fiber 树的可中断渲染。首先我们明确一点 task 本身采用最小堆根据 sortIndex 也即 expirationTime。并通过
peek 方法从 taskQueue 中取出来最紧急的任务。
每次 while 循环的退出就是一个时间切片,详细看下 while 循环退出的条件,可以看到一共有两种方式可以退出
队列被清空:这种情况就是正常下情况。从
taskQueue队列中获取下一个最紧急的任务来执行,如果这个任务为 null,则表示此任务队列被清空。退出workLoop循环任务执行超时:在执行任务的过程中由于任务本身过于复杂在执行
task.callback之前就会判断是否超时(shouldYieldToHost)。 如果超时也需要退出循环交给performWorkUntilDeadline发起下一次调度,与此同时浏览器可以有空闲执行别的任务。 因为本身MessageChannel监听事件是一个异步任务,故可以理解在浏览器执行完别的任务后会继续执行performWorkUntilDeadline
超时判断条件
currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime:首先会判断当前任务的过期时间是否大于当前时间,大于则说明当前任务还没有过期不用现在执行,先将执行权让给已过期的任务。!hasTimeRemaining:表示是否还有剩余时间,剩余时间不足则需要中断当前任务,让其他任务先执行,hasTimeRemaining一直为true,我们可以暂时忽略这个条件。
shouldYieldToHost 函数:
function shouldYieldToHost() {
const timeElapsed = getCurrentTime() - startTime;
if (timeElapsed < frameInterval) {
return false;
}
if (enableIsInputPending) {
if (needsPaint) {
return true;
}
if (timeElapsed < continuousInputInterval) {
if (isInputPending !== null) {
return isInputPending();
}
} else if (timeElapsed < maxInterval) {
if (isInputPending !== null) {
return isInputPending(continuousOptions);
}
} else {
return true;
}
}
return true;
}首先检查当前任务的使用时间是否小于帧间隔时间,小于则返回 false 表示无需中断,
startTime 是在调用 performWorkUntilDeadline 时赋的值,也就是任务开始调度的时候的开始时间:
const performWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
...
startTime = currentTime;
...
};如果大于表示当前任务的执行时间超过了一帧渲染的时间5ms,会让用户操作造成卡顿,则返回 true 表示需要中断。
关于 isInputPending 它的作用是检测用户的输入事件,例如:鼠标点击,键盘输入等,如果有用户输入测返回 true,没有则返回 false。
循环执行任务
接下来则是执行任务:
const callback = currentTask.callback;
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
//回到函数为null,则表示任务执行完成,会从任务队列中删除
currentTask.callback = null;
//获取任务的优先级
currentPriorityLevel = currentTask.priorityLevel;
//判断当前任务是否过期
const didUserCallbackTimeout = currentTask.expirationTime <= currentTime;
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskRun(currentTask, currentTime);
}
//获取执行任务完成后的结果
const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout);
currentTime = getCurrentTime();
if (typeof continuationCallback === 'function') {
currentTask.callback = continuationCallback;
} else {
if (currentTask === peek(taskQueue)) {
pop(taskQueue);
}
}
//检查延时队列中是否有过期的任务
advanceTimers(currentTime);
} else {
//删除当前任务
pop(taskQueue);
}首先从 currentTask 当前任务中获取任务执行函数 callback
callback 实际就是调用 scheduleCallback 时传入的 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 函数:
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) {
...
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
...
}然后判断了 callback 的类型 是否为 function ,如果不是则会从 taskQueue 中删除该任务,如果是则会执行该回调函数,然后回调函数返回执行结果 continuationCallback , continuationCallback 可以看作为当前任务的执行状态,当 continuationCallback 值为 null 时则表示当前任务执行完成,如果为 function 则表示当前任务未执行完成,在执行过程中被打断,需要先要让出执行权给优先级更高的任务先执行。
判断单个任务的状态
那么执行执行状态如果判断的呢?
首先我们先来看回顾一下调用 scheduleCallback 的函数 ensureRootIsScheduled 中的源码:
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) {
...
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;
}可以看到,调用 scheduleCallback 函数后会将任务对象 newTask 返回回来,并 挂载到 root 的 callbackNode 属性上
接下来我们进入 callback 函数中,也就是 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 中看一下具体是如果判断执行状态的:
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root, didTimeout) {
const originalCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
...
let exitStatus =
shouldTimeSlice(root, lanes) &&
(disableSchedulerTimeoutInWorkLoop || !didTimeout)
? renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes)
: renderRootSync(root, lanes);
if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) {
return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root);
}
return null;
}从源码中我们看到,首先将 root.callbackNode 赋值给了 originalCallbackNode 变量,中间会调用 renderRootConcurrent 或者 renderRootSync 方法, 那么我们可以判定到 root.callbackNode 肯定会在这两个方法中被消耗掉。
然后可以看到 root.callbackNode 在 commit 阶段 被置为了 null :
function commitRootImpl(root, renderPriorityLevel) {
...
root.callbackNode = null;
root.callbackPriority = NoLane;
...
}react 整个构建流程大致可以分为两个阶段:
render阶段,在这个阶段任务是可以被中断的commit阶段,这个阶段任务是无法被中断的
我们回过头再来看一下 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 函数中的代码:
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root, didTimeout) {
...
if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) {
return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root);
}
return null;
}如果当 任务执行到 commit 阶段 ,那么任务肯定已经完成了, root.callbackNode 会被置为null ,那么 if 判断肯定是不相等的,所以会返回null, 那么 workLoop 中的 continuationCallback 的值也会置为 null ,表示任务已执行完成。
那么任务在执行过程中被中断了呢?
我们来看一下并发渲染函数 renderRootConcurrent :
function renderRootConcurrent(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) {
...
do {
try {
workLoopConcurrent();
break;
} catch (thrownValue) {
handleError(root, thrownValue);
}
} while (true);
...
}其内部调用了 workLoopConcurrent 函数:
function workLoopConcurrent() {
while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield()) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}可以看到这个函数在循环创建 workInProgress 树 ,并且调用了 shouldYield 函数,之前我们有解析过 shouldYield 函数中主要是检查当前任务的执行时间是否大于一帧所渲染的时间, 并且会使用 isInputPending API来判断用户是否对页面有交互,如果满足其中一个条件则会中断当前任务。中断任务则不会继续向下执行,也就 不会执行到 commit 阶段 , root.callbackNode 会也不会被置为 null 。
那么 root.callbackNode 则会等于 originalCallbackNode ,那么就会进入 if 判断返回 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 函数。
那么我们回过头再看一下 workLoop 中的代码:
//获取执行任务完成后的结果
const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout);
currentTime = getCurrentTime();
if (typeof continuationCallback === 'function') {
currentTask.callback = continuationCallback;
}
//检查延时队列中是否有过期的任务
advanceTimers(currentTime);
currentTask = peek(taskQueue);当前任务未完成时,是不会从 taskQueue 中删除的,而是会将返回的函数 continuationCallback 重新赋值给当前任务的 callback 属性,然后会检查在执行过程中是否有过期的任务需要执行,有的话则会添加到 taskQueue 中。
如果当前任务是由于执行时间过长导致中断的话,peek(taskQueue) 取出的还是上一个未完成执行的任务,会继续执行。
如果是由于高优先级的任务导致的中断,peek(taskQueue) 取出的则是优先级最高的任务来执行。
当 currentTask 为 null 或者是被判断任务的条件所中断:
while (
currentTask !== null &&
!(enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused)
) {
if (
currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime &&
(!hasTimeRemaining || shouldYieldToHost())
) {
break;
}
...
}那么就走到下面:
if (currentTask !== null) {
return true;
} else {
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
return false;
}当 currentTask 不为 null 时,返回 true,表示 taskQueue 中还有任务,需要继续调度。
当 currentTask 为 null 时,返回 false,则表示 taskQueue 中所有任务都执行完成了,这时需要检查 timeQueue 中是否还有任务,有的话则需要在 timeQueue 中的第一个的任务过期时, 将改任务添加值 taskQueue 中,并且由于此时上一个调度已经结束了,所以需要重新创建一个调度者发起任务调度:
function handleTimeout(currentTime) {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = false;
advanceTimers(currentTime);
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled) {
if (peek(taskQueue) !== null) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
} else {
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
}
}
}我们在看向 performWorkUntilDeadline 函数 ,当 workLoop 执行完成时,会将返回值赋值给 hasMoreWork :
const performWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
try {
//调用scheduledHostCallback函数,开始任务的执行 scheduledHostCallback = flushWork
hasMoreWork = scheduledHostCallback(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime);
} finally {
if (hasMoreWork) {
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline();
} else {
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
scheduledHostCallback = null;
}
}
}当 hasMoreWork 为 true 时,则表示还有任务未执行,需要重新创建一个调度者,发起任务调度。
当 hasMoreWork 为 false 时,则表示所有任务都执行完成了,将 isMessageLoopRunning 和 scheduledHostCallback 重置,为下一次调度做好准备。
走到这里整个 Scheduler 的调度流程就结束了。
总结
Scheduler 用任务优先级去实现多任务的管理,优先解决高优任务,用任务的持续调度来解决时间片造成的单个任务中断恢复问题。 任务函数的执行结果为是否应该结束当前任务的调度提供参考,另外,在有限的时间片内完成任务的一部分,也为浏览器响应交互与完成任务提供了保障。