状态更新调度源码解析
前言
在前面几节,我们介绍了 React 中,状态更新的主要流程,以及 concurrent 模式下,优先级的概念以及优先级更新的流程,本节我们将从源码的角度来解析 React 是如何实现状态更新的。
无论是 setState 还是 useState 进行的更新,都会创建更新任务,也就是创建 Update 对象,并添加到 Fiber 的 UpdateQueue 中,如果是 Function Component 会添加到 baseQueue 中。
接下来就会进入核心的 reconciler 阶段,主要分为 4 个子阶段
- 任务输入:触发的更新都会 dispatch 到
scheduleUpdateOnFiber这个函数中,来处理更新任务 - 调度任务:通过
Scheduler来调度任务,等待空闲时间回调 - 执行任务会调:构造 Fiber 树,
render阶段的completeWork阶段会创建 Fiber 对应的 DOM 节点 - 输出 DOM 节点:
commit阶段会与渲染器交互,渲染出 DOM 节点
对于不同形式触发的状态更新来说,它们都会进入一套相同的 render 到 commit 的流程,这是因为在每次更新时都会创建一个保存更新状态相关内容的对象 Update。在 render 阶段的 beginWork 中会根据 Update 来计算 newState
在初始化阶段完成之后,如果触发了 state 的更新,那么会发生什么呢?
触发更新
以 useState 和 setState 来分别看函数组件和类组件的更新流程
类组件
触发 setState本质上是调用了 enqueueSetState
enqueueSetState(inst,payload,callback){
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);
...
enqueueUpdate(fiber, update, lane);
...
const root = scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}函数组件
对于函数组件而言,会调用 dispatchSetState
function dispatchSetState(fiber, queue, action) {
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
action,
hasEagerState: false,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
...
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}无论是通过什么方式来触发,都会创建一个 Update 对象,这样验证了我们之前一直所说的,然后它会被保存到环状链表 pending 中,最后都是会调用 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 方法,这个也就是整个更新的入口,接下来我们看看它都做了些什么
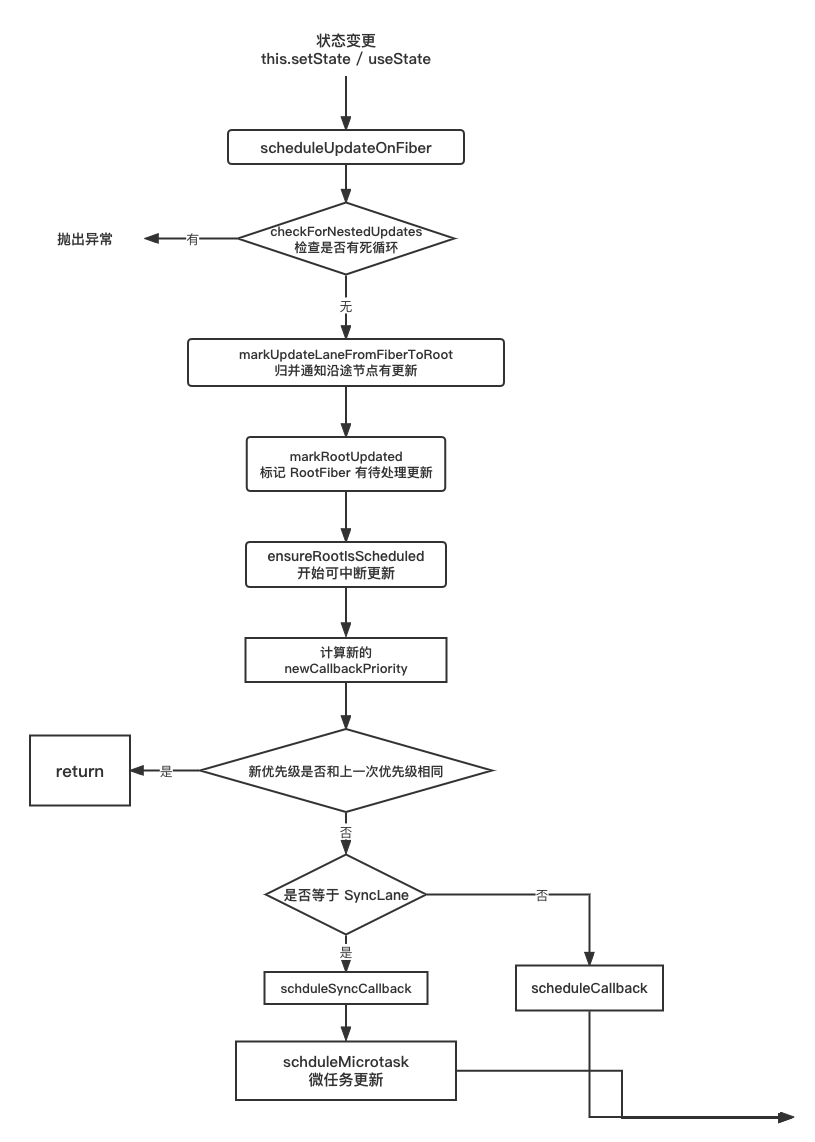
更新入口 scheduleUpdateOnFiber
从前面我们知道了,无论是什么方式触发的更新,最后都会调用 scheduleUpdateOnFiber方法,这也是任务调度的入口,它的核心流程如下
- 首先会检查当前的更新是否存在嵌套更新
- 递归向上通知沿途的父节点,子节点存在某种优先级的更新
- 标记 RootFiber 有待处理的更新,为 render 阶段做准备
- 开始可中断更新
// react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.new.js
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(
fiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
eventTime: number,
): FiberRoot | null {
// 检查是否有死循环
checkForNestedUpdates();
...
// 自底向上标记更新优先级
const root = markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(fiber, lane);
...
// 标记 root 有更新,lane 插入到 root.pendingLanes 中
markRootUpdated(root, lane, eventTime);
...
if (root === workInProgressRoot) {
// 在渲染过程中接收到一个更新,在根节点上标记一个交错更新,
if (
deferRenderPhaseUpdateToNextBatch ||
(executionContext & RenderContext) === NoContext
) {
workInProgressRootUpdatedLanes = mergeLanes(
workInProgressRootUpdatedLanes,
lane,
);
}
if (workInProgressRootExitStatus === RootSuspendedWithDelay) {
// 执行高优先级更新
markRootSuspended(root, workInProgressRootRenderLanes);
}
}
// 执行可中断更新
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
...
return root;
}1.检查是否死循环 checkForNestedUpdates
在 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 函数中,首先会调用 checkForNestedUpdates 方法,检查是否有嵌套更新,也可以说是循环更新,无限调用,这种情况会抛出异常
这里的 NESTED_UPDATE_LIMIT 的值是 50,也就是说当循环次数超过 50 次时,会认为是死循环,会抛出错误
function checkForNestedUpdates() {
if (nestedUpdateCount > NESTED_UPDATE_LIMIT) {
nestedUpdateCount = 0;
rootWithNestedUpdates = null;
throw new Error(
'Maximum update depth exceeded. This can happen when a component ' +
'repeatedly calls setState inside componentWillUpdate or ' +
'componentDidUpdate. React limits the number of nested updates to ' +
'prevent infinite loops.',
);
}
}2.递归向上通知 parent 有更新 markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot
接下来,会调用 markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot 方法,更新当前 Fiber 节点的 lanes 字段,并向上归并在父节点的 childLanes 字段中添加为本次更新的优先级 lanes。最后返回当前的 rootFiber 节点
注意这里会对 Fiber 节点的 alternate Fiber 的 lane 进行更新,这个非常重要,下一节会讲到
function markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(
sourceFiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
): FiberRoot | null {
// 更新当前 Fiber 的优先级
sourceFiber.lanes = mergeLanes(sourceFiber.lanes, lane);
let alternate = sourceFiber.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.lanes = mergeLanes(alternate.lanes, lane);
}
let node = sourceFiber;
let parent = sourceFiber.return;
// 归并更新 父节点 的优先级
while (parent !== null) {
parent.childLanes = mergeLanes(parent.childLanes, lane);
alternate = parent.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.childLanes = mergeLanes(alternate.childLanes, lane);
}
node = parent;
parent = parent.return;
}
if (node.tag === HostRoot) {
const root: FiberRoot = node.stateNode;
return root;
} else {
return null;
}
}这里采用 mergeLanes 来合并优先级,因为可能会有多个更新存在,都需要在后续进行调度,lanes 更新的操作很简单,只需要将当前的优先级 lane 与之前的 lane 进行二进制或运算即可
export function mergeLanes(a: Lanes | Lane, b: Lanes | Lane): Lanes {
return a | b;
}3. 标记 RootFiber 有待处理更新
接下来会将更新的 lane 通过二进制运算添加到 root Fiber 的 pendingLanes 中,在 root Fiber 标记一个更新
export function markRootUpdated(
root: FiberRoot,
updateLane: Lane,
eventTime: number,
) {
// 设置更新的优先级
root.pendingLanes |= updateLane;
if (updateLane !== IdleLane) {
root.suspendedLanes = NoLanes;
root.pingedLanes = NoLanes;
}
const eventTimes = root.eventTimes;
const index = laneToIndex(updateLane);
eventTimes[index] = eventTime;
}4. 开始可中断更新 ensureRootIsScheduled
在函数的最后,会调用 ensureRootIsScheduled 方法,传入已经被标记过的 root Fiber 节点以及创建 update 的时间,开始可中断更新
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);接下来详细看看 ensureRootIsScheduled 方法做了什么
注册调度任务
ensureRootIsScheduled 函数的作用是为 root 安排调度任务,每个更新任务的 update 都会经过 ensureRootIsScheduled 的处理,它主要会做以下几件事:
- 首先会计算最新的调度更新优先级
newCallbackPriority,判断是否和rootFiber上的calllbackPriority优先级是否相等,如果相等,则会因为优先级没有改变,重用当前任务,直接退出 - 如果不相等,会进入真正的调度任务函数
sheduleSyncCallback函数中 - 最后会将
newCallbackPriority赋值给callbackPriority
核心代码如下
// 注册任务
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) {
...
// 注册的新任务
let newCallbackNode;
// 如果新渲染任务的优先级是同步优先级
// if 逻辑处理的是同步任务,同步任务不需经过 Scheduler
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLane) {
// 同步任务不经过 Scheduler
if (root.tag === LegacyRoot) {
// Legacy 模式
scheduleLegacySyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
} else {
// 非 legacy模式
scheduleSyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
}
// React18 新增加的
if (supportsMicrotasks) {
scheduleMicrotask(() => {
if (executionContext === NoContext) {
flushSyncCallbacks();
}
});
} else {
scheduleCallback(ImmediateSchedulerPriority, flushSyncCallbacks);
}
...
} else {
...
// 调度优先级任务
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
}
...
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;
}如果任务是同步任务,就不需要 Scheduler 调度,直接通过 scheduleSyncCallback 和 scheduleLegacySyncCallback 处理,当 JS 主线程空闲的时候,则执行 performSyncWorkOnRoot 函数来执行同步任务
如果任务是并发任务,则需要经过 Scheduler 调度,会通过 scheduleCallback 回调函数注册调度任务。
开始调度任务
分为同步和并发两种情况来讨论
同步情况
当同步状态下触发多次 useState 的时候,会执行以下步骤
- 首先第一次进入到
ensureRootIsScheduled,计算出新的更新任务的优先级newCallbackPriority,和之前的callbackPriority进行对比,如果相等那就直接退出 - 同步状态下更新的优先级
newCallbackPriority是等于SyncLane的,那么会执行两个函数,scheduleSyncCallback和scheduleMicrotask。
最终都会进入 scheduleSyncCallback 的逻辑,这个方法非常简单,就是将任务放入 syncQueue 队列当中
export function scheduleSyncCallback(callback: SchedulerCallback) {
// 将任务放入队列中
if (syncQueue === null) {
syncQueue = [callback];
} else {
syncQueue.push(callback);
}
}接着会在下面的流程中通过 scheduleMicrotask 来执行 flushSyncCallbacks 方法,这个方法会立即执行更新队列,发起更新任务,目的就是让任务不延时到下一帧。同步情况也需要调度是为了保证更新的连续性,一个一个任务依次执行。
scheduleMicrotask(() => {
if (executionContext === NoContext) {
flushSyncCallbacks();
}
});scheduleMicrotask是一个 ployfill 实现,本质上就是一个 Promise.resolve 以及不兼容情况下使用的 setTimeout
export const scheduleMicrotask: any =
typeof queueMicrotask === 'function'
? queueMicrotask
: typeof localPromise !== 'undefined'
? callback =>
localPromise
.resolve(null)
.then(callback)
.catch(handleErrorInNextTick)
: scheduleTimeout; // TODO: Determine the best fallback here.异步情况
上面是在同步情况下的更新逻辑,有时候更新是在 setTimeout 等方法中触发的,那么他们会进入下面这些逻辑
- 首先会判断
existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority是否相等,来尝试复用它 - 接下来会执行
scheduleCallback,得到最新的newCallbackNode,赋值给root
scheduleCallback 会调用 Scheduler_scheduleCallback 方法,具体来看看这个方法的实现
function scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback) {
return Scheduler_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback);
}Scheduler_scheduleCallback 方法最终是由 unstable_scheduleCallback 方法导入的,这个方法在 scheduler/src/forks/scheduler.js目录下,比较难找
通过调用 unstable_scheduleCallback 方法创建调度任务,然后根据任务是否超时,将任务插入到超时队列 timerQueue 和调度任务队列 taskQueue
将任务插入调度任务队列 taskQueue 之后,会通过 requestHostCallback 函数去调度任务。
核心流程如下
- 通过
startTime和currentTime比较,来判断任务是否过期,过期存入taskQueue,未过期存入timerQueue - 如果有过期任务存在,并且没有正在调度的任务,那么通过 requestHostCallback 来调度
- 如果没有过期任务,通过
requestHostTimeout来延时执行
function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) {
// 获取当前时间戳
var currentTime = getCurrentTime();
var startTime;
...
// 根据调度优先级设置相应的超时时间
var timeout;
switch (priorityLevel) {
case ImmediatePriority:
timeout = IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case UserBlockingPriority:
timeout = USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case IdlePriority:
timeout = IDLE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case LowPriority:
timeout = LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case NormalPriority:
default:
timeout = NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
}
// 过期时间
var expirationTime = startTime + timeout;
...
// 表示这个任务将会延迟执行
if (startTime > currentTime) {
// 当前任务已超时,插入超时队列
newTask.sortIndex = startTime;
push(timerQueue, newTask);
if (peek(taskQueue) === null && newTask === peek(timerQueue)) {
// 这个任务是最早延迟执行的
if (isHostTimeoutScheduled) {
// 取消现有的定时器
cancelHostTimeout();
} else {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = true;
}
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime);
}
} else {
// 任务未超时,插入调度任务队列
newTask.sortIndex = expirationTime;
// taskQueue 是一个二叉堆结构,以最小堆的形式存储 task
push(taskQueue, newTask);
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskStart(newTask, currentTime);
newTask.isQueued = true;
}
// 符合更新调度执行的标志
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled && !isPerformingWork) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
}
}
return newTask;
}taskQueue里存放的是过期的任务,根据过期时间来排序,需要在调度的workLoop中循环执行完这些任务timerQueue里存的都是没有过期的任务,依据任务的开始时间(startTime)排序,在调度workLoop中 会用advanceTimers检查任务是否过期,如果过期了,放入taskQueue队列。
总结
至此状态更新的大致流程我们已经讲解完毕,后面省略了一部分关于 Scheduler 部分的内容,会在后面 Schduler 部分单独讲解
以下就是完整流程图